Let’s dive into ketogenic diets and their $33-billion gimmick.
The carbohydrate–insulin model of obesity, the underlying theory that ketogenic diets have some sort of metabolic advantage, has been experimentally falsified. Keto diet proponents’ own studies showed the exact opposite: Ketogenic diets actually put you at a metabolic disadvantage and slow the loss of body fat. How much does fat loss slow down on a low-carb diet?
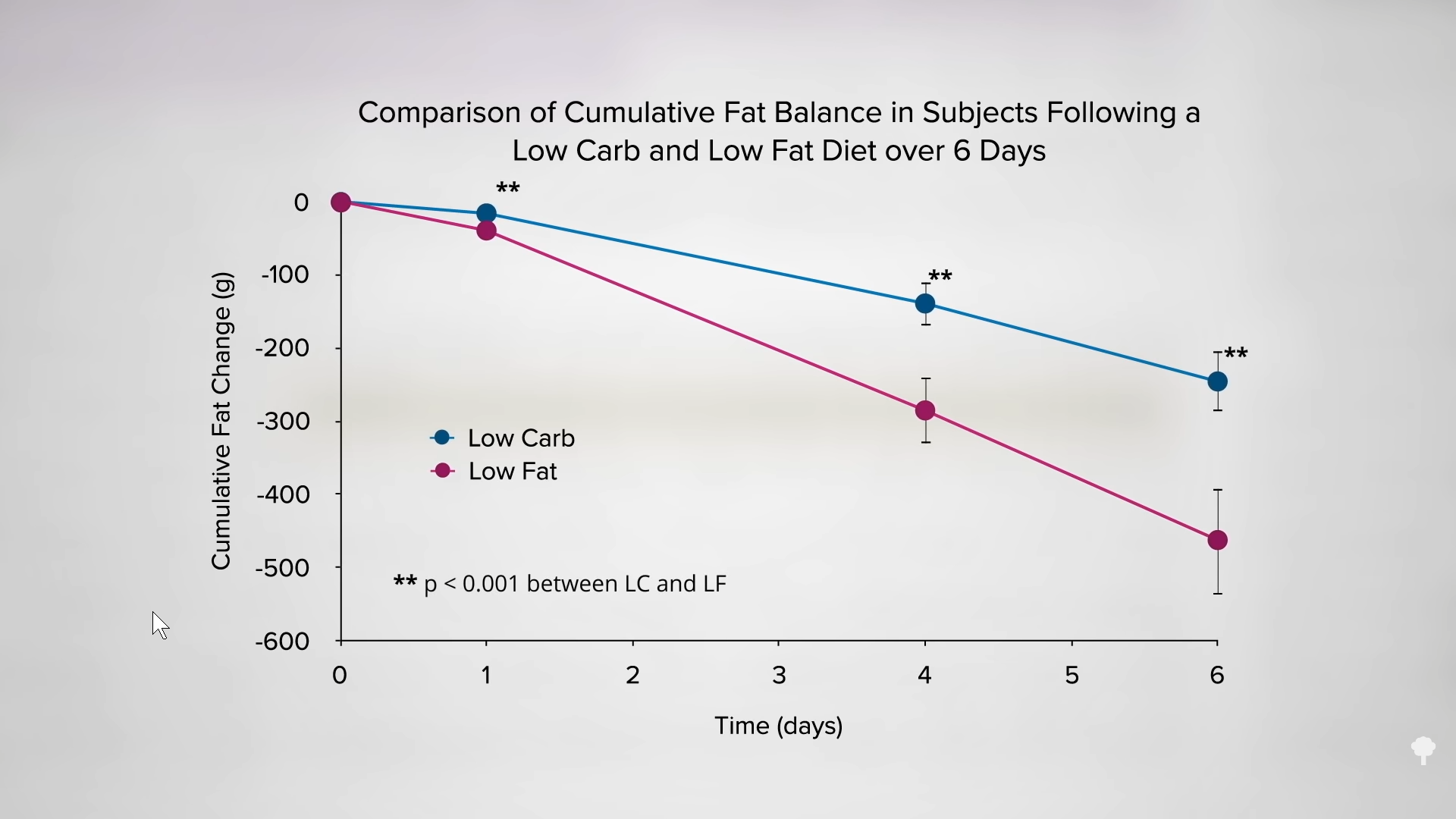
As I discuss in my video Keto Diet Results for Weight Loss, if you cut about 800 calories of carbohydrates from your diet a day, you lose 53 grams of body fat a day. But if you cut the same number of fat calories, you lose 89 grams of fat a day. Same number of calories cut, but nine butter pats’ worth of extra fat melting off your body each day on a low-fat diet, compared to a low-carb one. Same number of calories, but about 80 percent more fat loss when you cut down on fat instead of carbs. You can see a graph of these results below and at 1:07 in my video. The title of the study speaks for itself: “Calorie for Calorie, Dietary Fat Restriction Results in More Body Fat Loss Than Carbohydrate Restriction in People with Obesity.”
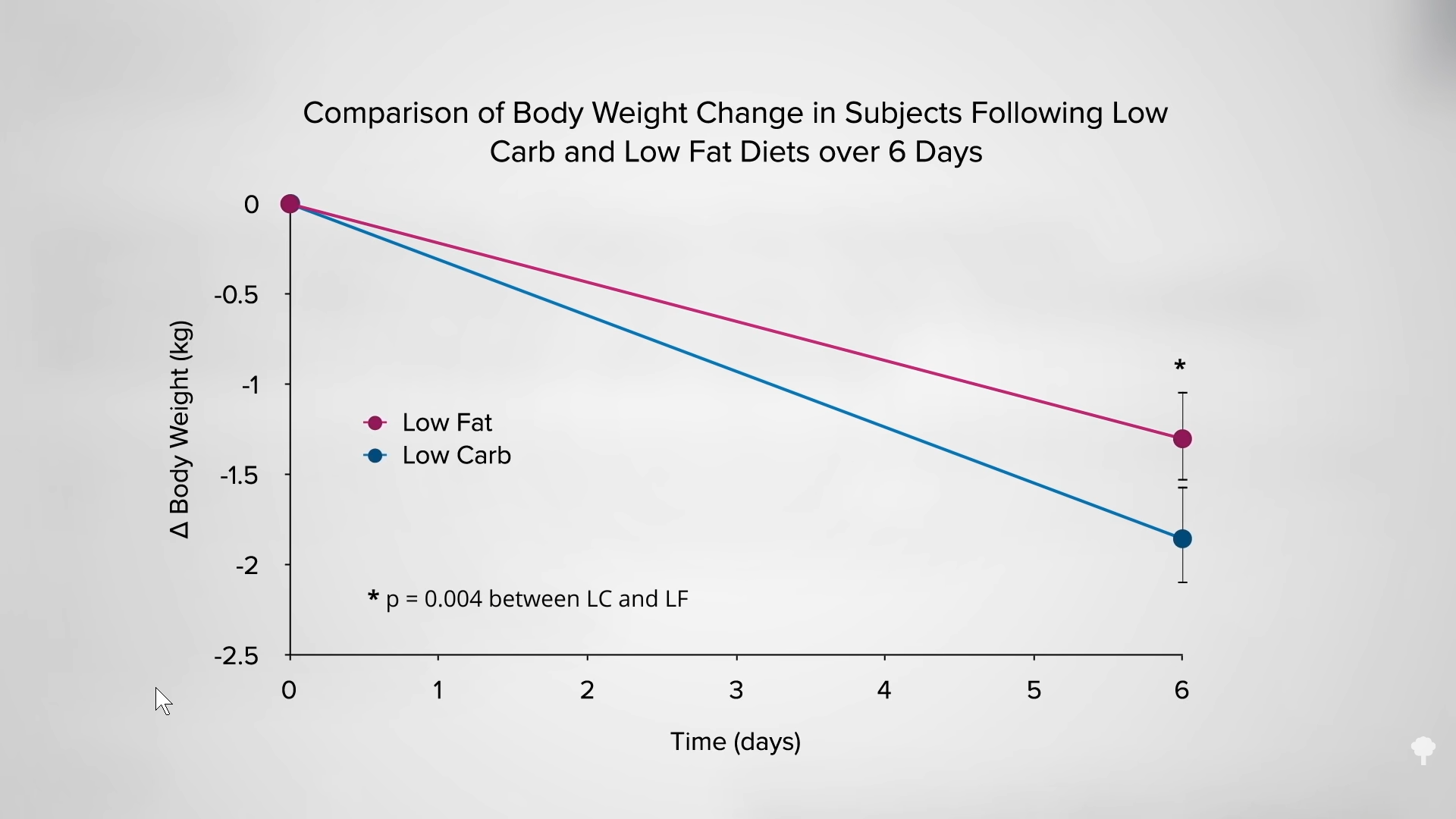
Just looking at the bathroom scale, though, would mislead you into thinking the opposite. After six days on the low-carb diet, study subjects lost four pounds. On the low-fat diet, they lost less than three pounds, as you can see in the graph below and at 1:40 in my video. So, according to the scale, it looked like the low-carb diet wins hands down. You can see why low-carb diets are so popular. What was happening inside their bodies, however, tells the real story. The low-carb group was losing mostly lean mass—water and protein. This loss of water weight helps explain why low-carb diets have “been such a persistent theme for authors of diet books and such ‘cash cows’ for publishers,” going back more than the last 150 years. That’s their secret. As one weight-loss expert noted, “Rapid water loss is the $33-billion diet gimmick.”
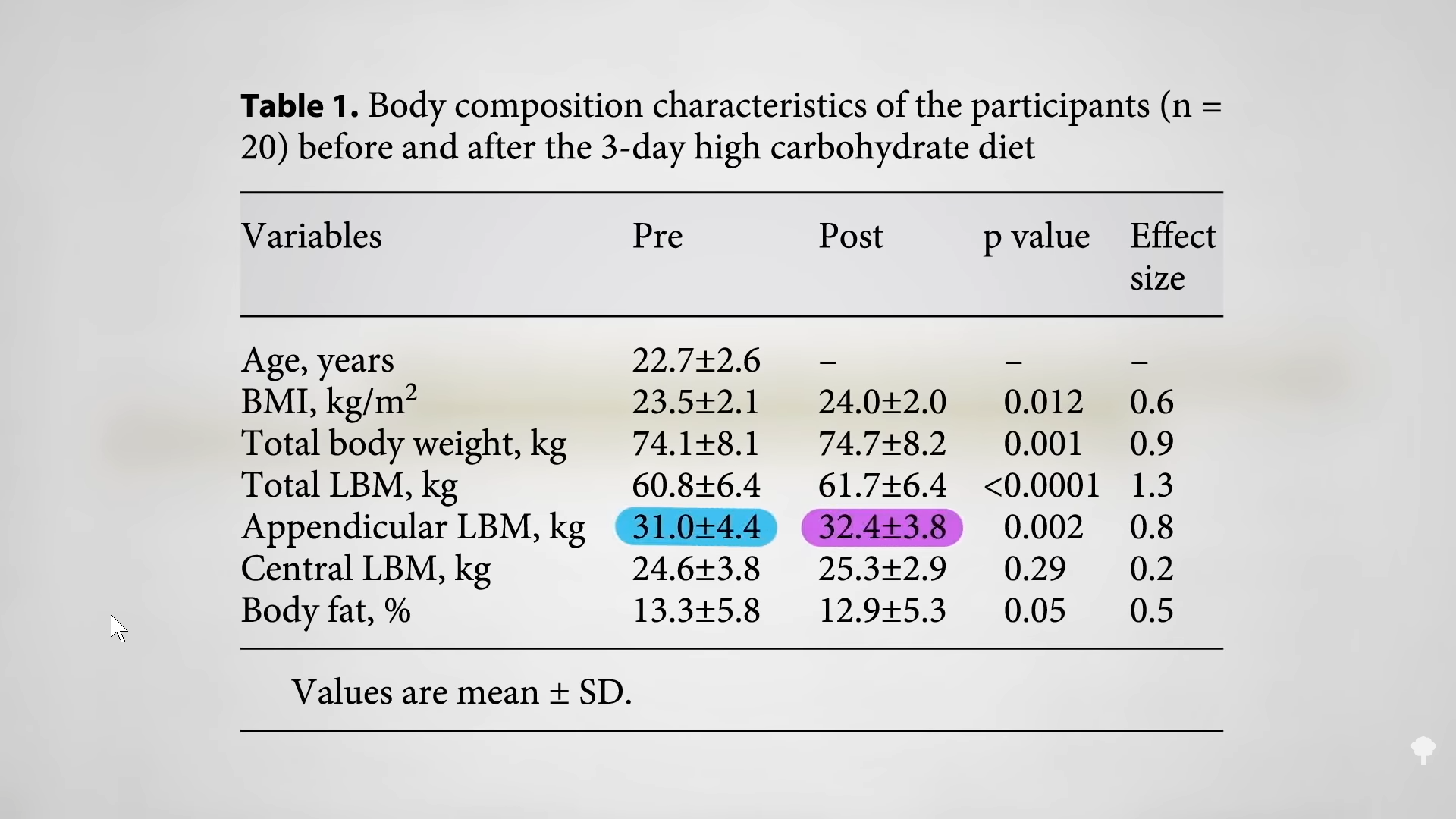
When you eat carbohydrates, your body bulks up your muscles with glycogen for quick energy. Eat a high-carbohydrate diet for three days, and you may add about three pounds of muscle mass onto your arms and legs, as you can see below and at 2:34 in my video. Those glycogen stores drain away on a low-carb diet and pull water out with it. (The ketones also need to be flushed out of the kidneys, pulling out even more water.) On the scale, that can manifest as four more pounds coming off within ten days, but that “was all accounted for by losses in total body water”—that is water loss.
The bottom line: Keto diets just don’t hold water.
The thrill of seeing the pounds come off so quickly on the scale keeps many coming back to the low-carb altar. When the diet fails, the dieters often blame themselves, but the intoxication of that initial, rapid weight loss may tempt them back, like getting drunk again after forgetting how terrible the last hangover was. This has been dubbed the “false hope syndrome.” “The diet industry thrives for two reasons—big promises and repeat customers,” something low-carb diets were built for, given that initial, rapid water loss.
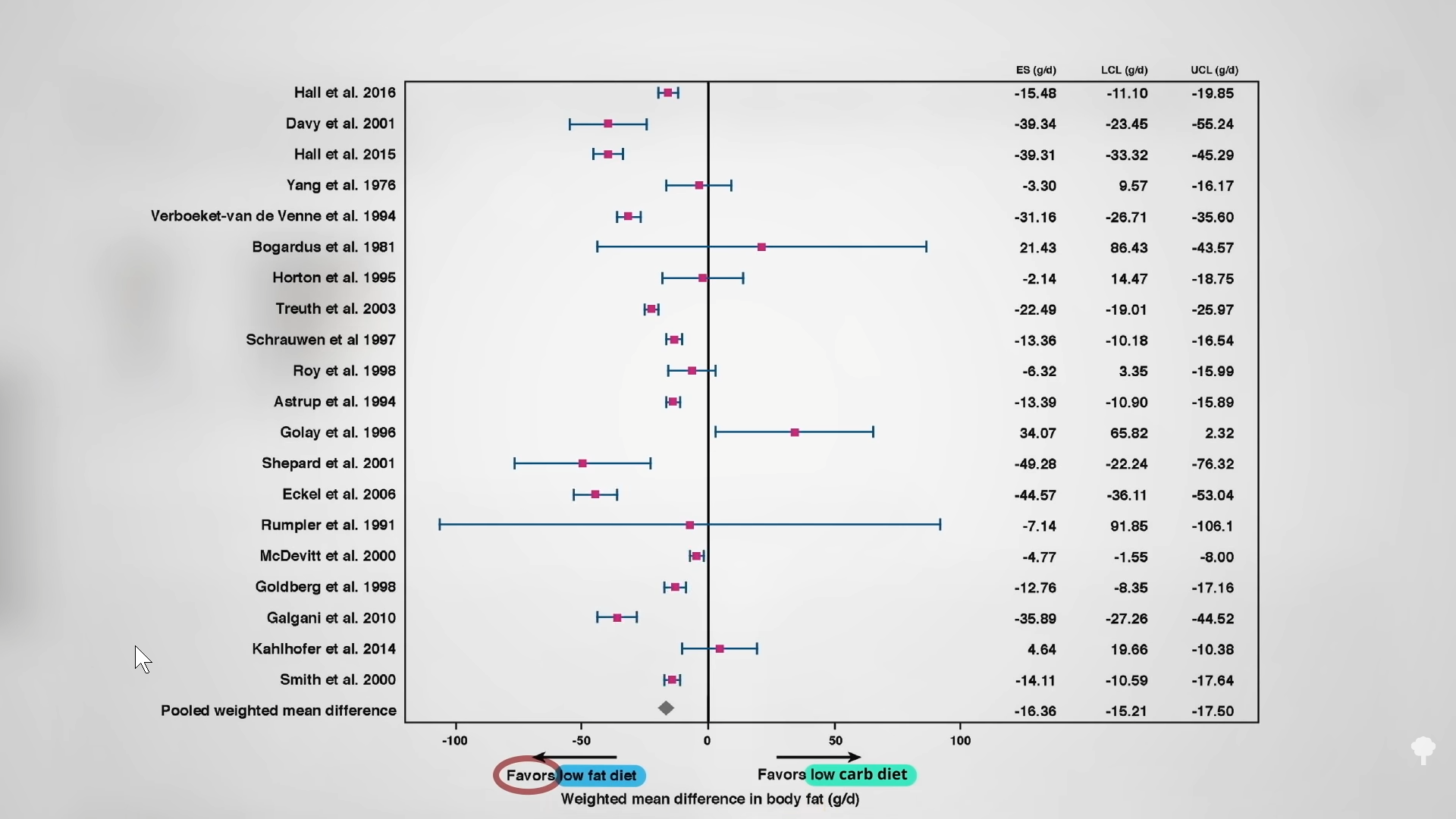
What we care about is body fat. In six days, the low-fat diet extracted a total of 80 percent more fat from the body than the low-carb diet. It’s not just one study either. As you can see below and at 3:54 in my video, you can look at all of the controlled feeding trials where researchers compared low-carb diets to low-fat ones, swapping the same number of carb calories for fat calories or vice versa. If a calorie is just a calorie, then all of the studies should have crossed that zero line in the middle, straddling “favors low-fat diet” and “favors low-carb diet,” and indeed six did. One study showed more fat loss on a low-carb diet, but every other study favored the low-fat diet—more loss of body fat eating the same number of calories. When you put all of the studies together, we’re talking 16 more grams of daily body fat lost on the low-fat diets. That’s like four more pats of butter melting off your body on a daily basis. Less fat in the mouth means less fat on the hips, even when you’re taking in the same number of calories.
 This is the third installment of my seven-part series on keto diets.
This is the third installment of my seven-part series on keto diets.
This keto research came from the deep dive I took for my book How Not to Diet. (All proceeds I receive from my books are donated to charity.) You can learn more about How Not to Diet and order it here. Also please feel free to check out some of my popular weight-loss videos in related videos below.














